React Native Apps That Can Draw Over Other Apps
React Native Activity Demo
Build Status
| Android | iOS |
|---|---|
| | |
This sample, which grew out of a question on Stack Overflow, demonstrates the interface between React Native JavaScript and native code – Java on Android, Objective-C on iOS.
The original version was Android-only; support for iOS was added in March 2019.
This project demonstrates the following:
- Calling from JavaScript into native modules:
- ...using a custom native module called
ActivityStarter:- Navigate from React Native to a Java activity (or iOS view controller) internal to the host app;
- Start an external intent to dial a phone number, passing data from JavaScript;
- Query the host app for information.
- ...using the native module
Clipboard, which comes with React Native out of the box:- Copy information to the clipboard.
- ...using a custom native module called
- Calling a JavaScript method from Java or Objective-C, using an officially undocumented approach.
- Sending events from the native platform to JavaScript. (When possible, prefer this approach to the undocumented one.)
- Verifying that custom edit menu extensions work with React Native
TextInput. (Android only.) - Adding a custom menu option to React Native debug menu.
There is no technical difference between the ActivityStarter and Clipboard native modules, except one is defined in this project while the other ships as part of React Native.
The starting point for this sample is a slightly tweaked standard React Native project as generated by a long-outdated version of react-native init. We add six buttons to the generated page:
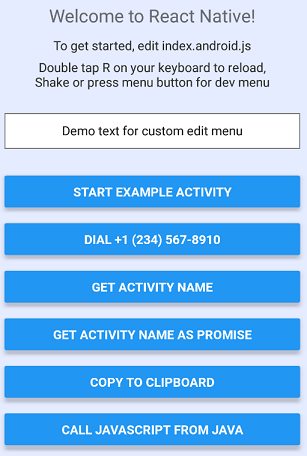
The TextInput box appears only in the Android version. Since both platforms use the same JavaScript, I took the opportunity to demonstrate how to handle platform-specific tweaks – look for Platform.select in index.js.
Getting started
- Install Git.
- Install Node.js.
- Install Yarn. Use a shell with Git, Node and Yarn in the path for all commands.
- Clone this project:\
git clone https://github.com/petterh/react-native-android-activity.git\ (Alternatively, create your own fork and clone that instead.) -
cd react-native-android-activity - Run
yarnto download dependencies (or, if you wish,npm install) - For Android development (using Windows, Mac or Linux), install Android Studio (follow instructions on this page).
- For iOS development (Mac only), install Xcode.
- By default, the debug build of the app loads the JS bundle from your dev box, so start a bundler:
yarn start
Android
- Connect an Android device via USB, or use an emulator.
- Enable USB Debugging in Developer options.
- Open the app in Android Studio and run it.
- If this fails with the message "Could not get BatchedBridge, make sure your bundle is packaged correctly", your packager is likely not running.
- If it complains about connecting to the dev server, run
adb reverse tcp:8081 tcp:8081 - If it crashes while opening the ReactNative controls, try to modify the following phone settings: Android Settings -> Apps -> Settings once again (the gear) to go to Configure Apps view -> Draw over other apps -> Allow React Native Android Activity Demo to draw over other apps. (The demo app should ask for this automatically, though.)
- To embed the bundle in the apk (and not have to run the packager), set
bundleInDebug=trueinandroid/gradle.properties.
iOS
- Open the iOS project in Xcode:
open Activity.xcworkspace. - Run the Activity application.
The React Native side
The gist of the JavaScript code looks like this:
import { ... , NativeModules , ... } from 'react-native' ; export default class ActivityDemoComponent extends Component { render ( ) { return ( < View style= {styles. container } > < Text style= {styles. welcome } > Welcome to React Native ! < / Text > < Text style= {styles. instructions } > To get started, edit index. js < / Text > < ! -- Menu buttons: https: / /facebook. github . io /react-native/docs/debugging -- > < Text style= {styles. instructions } > Double tap R on your keyboard to reload, { '\n' } Shake or press menu button for dev menu < / Text > < View style= {styles. buttonContainer } > < Button onPress= { ( ) => NativeModules . ActivityStarter . navigateToExample ( ) } title= 'Start example activity' / > < Button onPress= { ( ) => NativeModules . ActivityStarter . dialNumber ( '+1 (234) 567-8910' ) } title= 'Dial +1 (234) 567-8910' / > < Button onPress= { ( ) => NativeModules . ActivityStarter . getName ( ( name ) => { alert (name) ; } ) } title= 'Get activity name' / > < Button onPress= { ( ) => NativeModules . Clipboard . setString ( "Hello from JavaScript!" ) } title= 'Copy to clipboard' / > < / View > < / View > ) ; } } The first three buttons use three methods on NativeModules.ActivityStarter. Where does this come from?
Android: The Java module
ActivityStarter is just a Java class that implements a React Native Java interface called NativeModule. The heavy lifting of this interface is already done by BaseJavaModule, so one normally extends either that one or ReactContextBaseJavaModule:
class ActivityStarterModule extends ReactContextBaseJavaModule { ActivityStarterModule ( ReactApplicationContext reactContext) { super (reactContext) ; } @Override public String getName ( ) { return "ActivityStarter" ; } @ReactMethod void navigateToExample ( ) { ReactApplicationContext context = getReactApplicationContext ( ) ; Intent intent = new Intent (context, ExampleActivity . class ) ; context. startActivity (intent) ; } @ReactMethod void dialNumber ( @NonNull String number) { Intent intent = new Intent ( Intent .ACTION_DIAL, Uri . parse ( "tel:" + number) ) ; getReactApplicationContext ( ) . startActivity (intent) ; } @ReactMethod void getActivityName ( @NonNull Callback callback) { Activity activity = getCurrentActivity ( ) ; if (activity != null ) { callback. invoke (activity. getClass ( ) . getSimpleName ( ) ) ; } } } The name of this class doesn't matter; the ActivityStarter module name exposed to JavaScript comes from the getName() method.
Each method annotated with a @ReactMethod attribute is accessible from JavaScript. Overloads are not allowed, though; you have to know the method signatures. (The out-of-the-box Clipboard module isn't usually accessed the way I do it here; React Native includes Clipboard.js, which makes the thing more accessible from JavaScript – if you're creating modules for public consumption, consider doing something similar.)
A @ReactMethod must be of type void. In the case of getActivityName() we want to return a string; we do this by using a callback.
Android: Connecting the dots
The default app generated by react-native init contains a MainApplication class that initializes React Native. Among other things it extends ReactNativeHost to override its getPackages method:
@Override protected List < ReactPackage > getPackages ( ) { return Arrays . < ReactPackage > asList ( new MainReactPackage ( ) ) ; } This is the point where we hook our Java code to the React Native machinery. Create a class that implements ReactPackage and override createNativeModules:
class ActivityStarterReactPackage implements ReactPackage { @Override public List < NativeModule > createNativeModules ( ReactApplicationContext reactContext) { List < NativeModule > modules = new ArrayList < > ( ) ; modules. add ( new ActivityStarterModule (reactContext) ) ; return modules; } @Override public List < Class < ? extends JavaScriptModule > > createJSModules ( ) { return Collections . emptyList ( ) ; } @Override public List < ViewManager > createViewManagers ( ReactApplicationContext reactContext) { return Collections . emptyList ( ) ; } } Finally, update MainApplication to include our new package:
public class MainApplication extends Application implements ReactApplication { private final ReactNativeHost mReactNativeHost = new ReactNativeHost ( this ) { @Override public boolean getUseDeveloperSupport ( ) { return BuildConfig .DEBUG; } @Override protected List < ReactPackage > getPackages ( ) { return Arrays . < ReactPackage > asList ( new ActivityStarterReactPackage ( ) , // This is it! new MainReactPackage ( ) ) ; } } ; @Override public ReactNativeHost getReactNativeHost ( ) { return mReactNativeHost; } @Override public void onCreate ( ) { super . onCreate ( ) ; SoLoader . init ( this , false ) ; } } Android: Calling JavaScript from Java
This demo is invoked by the last button on the page:
< Button onPress= { ( ) => NativeModules . ActivityStarter . callJavaScript ( ) } title= 'Call JavaScript from Java' / > The Java side looks like this (in ActivityStarterReactPackage class):
@ReactMethod void callJavaScript ( ) { Activity activity = getCurrentActivity ( ) ; if (activity != null ) { MainApplication application = ( MainApplication ) activity. getApplication ( ) ; ReactNativeHost reactNativeHost = application. getReactNativeHost ( ) ; ReactInstanceManager reactInstanceManager = reactNativeHost. getReactInstanceManager ( ) ; ReactContext reactContext = reactInstanceManager. getCurrentReactContext ( ) ; if (reactContext != null ) { CatalystInstance catalystInstance = reactContext. getCatalystInstance ( ) ; WritableNativeArray params = new WritableNativeArray ( ) ; params. pushString ( "Hello, JavaScript!" ) ; catalystInstance. callFunction ( "JavaScriptVisibleToJava" , "alert" , params) ; } } } The JavaScript method we're calling is defined and made visible to Java as follows:
import BatchedBridge from "react-native/Libraries/BatchedBridge/BatchedBridge" ; export class ExposedToJava { alert ( message ) { alert (message) ; } } const exposedToJava = new ExposedToJava ( ) ; BatchedBridge . registerCallableModule ( "JavaScriptVisibleToJava" , exposedToJava) ; Android: Summary
- The main application class initializes React Native and creates a
ReactNativeHostwhosegetPackagesinclude our package in its list. -
ActivityStarterReactPackageincludesActivityStarterModulein its native modules list. -
ActivityStarterModulereturns "ActivityStarter" from itsgetNamemethod, and annotates three methods with theReactMethodattribute. - JavaScript can access
ActivityStarter.getActivityNameand friends viaNativeModules.
iOS
The iOS Objective-C classes are parallel to the Android Java classes. There are differences:
- Modules are picked up automatically.
- There is no react application context; instead there is the react native bridge, which is initialized in the
AppDelegateclass. - Events are done somewhat differently. In Android we can just grab a
DeviceEventManagerModule.RCTDeviceEventEmitterand fire away; in iOS it is necessary to subclassRCTEventEmitter.
Here is a sample of an Objective-C class implementation with methods callable from JavaScript:
@implementation ActivityStarterModule RCT_EXPORT_MODULE(ActivityStarter); RCT_EXPORT_METHOD(navigateToExample) { dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ AppDelegate *appDelegate = (AppDelegate *) [UIApplication sharedApplication].delegate; [appDelegate navigateToExampleView]; }); } RCT_EXPORT_METHOD(getActivityName:(RCTResponseSenderBlock) callback) { callback(@[@"ActivityStarter (callback)"]); } @end iOS: Calling JavaScript from Java
This requires the react native bridge, so responsibility resides with the AppDelegate class, for convenience.
- (void) callJavaScript { [self.reactBridge enqueueJSCall:@"JavaScriptVisibleToJava" method:@"alert" args:@[@"Hello, JavaScript!"] completion:nil]; } Addendum
I just added a second version of ActivityStarterModule.getActivityName called getActivityNameAsPromise, with a corresponding button.
Addendum 2
I added a sample of event triggering, another way to communicate. Tap Start Example Activity, then Trigger event.
Further reading
- Native Modules on Android
- Native Modules on iOS
Issues
The various Android apps explicitly call SoLoader.init because of this issue. I have a PR to fix it. Once this is in (assuming Facebook accepts it) I'll remove them.
React Native Apps That Can Draw Over Other Apps
Source: https://nicedoc.io/petterh/react-native-android-activity
0 Response to "React Native Apps That Can Draw Over Other Apps"
Post a Comment